Wang Weiwu1, Fu Bo2, Qunwu Li3, Qin Shuanglin4, Yao Hui4, Lu Yufei4, Chen Qi4, Ge Tingting4, Jiang Qiong2, Rao Zhiwei2, Min Qing4*
1Hunan Ruitongtang Medical Co. Ltd., Changsha, Hunan, 437100, lepuswei@gmail.com
2TCM department, Xianning Centreal Hospital, Xianning, Hubei, 437500, 524958229@qq.com
3The second affiniated hospital of Hubei College of Science and Technology, Xianning, Hubei, 437500
4School of Pharmacy, Hubei College of Science and Technology, baimin0628@163.com
*Corresponding Author: Min Qing, School of Pharmacy, Hubei College of Science and Technology, baimin0628@163.com
Abstract
The COVID‐19 pandemic spreads rapidly and wildly around the world. While the coronavirus outbreak poses health risks for everyone, it is mainly challenging for senior houses and psychiatric hospitals because of community characteristics. A practical clinical path has not yet been promulgated for preventing and treating COVID-19 in those particular communities. Herein, we presented a successful practice of Chinese herb decoction FeiDuQing (FDQ) in treating extensive community cluster infection of COVID-19 for a specific population. This is also the first reported case of cure cluster infection of COVID-19 using Chinese medicine as the only therapeutic regime.
In this cluster, infection developed in a mental disorder center and adjacent senior care center. Sixty patients were confirmed infected by nucleic acid test. Following management through interventions such as taking FDQ daily, immediate reporting, centralized separation in different zones, and enforcement of hygiene and disinfection, none of the other patients was infected, and all the confirmed infections were cured.
Introduction
COVID-19, a respiratory disease caused by a new coronavirus strain, has killed more than 489,000 people worldwide since June 25 [1]. Poor and vulnerable populations and patients with serious mental illness may be among the most brutal hit [2]. Mental disorders patients in psychiatric hospitals are more vulnerable to COVID-19 infection because of their disordered mental state, poor control and self-care, and because they commonly participate in group activities which increase contact.
Many cluster infection cases were reported in psychiatric hospitals worldwide [3,4,5]. As of April 17th, NBC News had identified more than 1,450 COVID-19 cases at state mental health facilities in 23 states and Washington, D.C. [6].
However, isolating and treating mental disorders in COVID-19 patients is an ethical and practical challenge [7].
FeiDuQing (FDQ) is formulated by 12 herbs: Divaricate saposhniovia root, stir-fried atractylodes macrocephala, Houttuynia cordtata thumb, Radix paeoniae rubra, Chinese thorowax root, Platycodon grandiflorum, Fritillaria acuminate, Winter mulberry leaf, Ramulus Cinnamomi, Stir fried white paeony root, Radix Isatidis, Glycyrrhiza uralensis. It has been widely and successfully used in hospitals in Xianning City to treat COVID-19 patients. FDQ has proved the effectiveness of a 98.21 % cure rate in Xianning City, the first prefecture-level city in Hubei Province that cured all COVID-10 patients ([8,9] another paper by Dr. Weiwu Wang).
On Feb 9, 2020, a significant cluster infection of COVID-19 was reported in a mental care center and an adjacent senior-care center in Xianning City, Hubei Province in China. On the report day, 60 patients were detected as COVID-19 nucleic acid positive. Meanwhile, symptoms like cough, fever, and headache were observed in succession. Due to the shortage of medical equipment and medication and the population specialty, how to treat those patients became complicated. Finally, we decided to use FDQ as the only treatment for those patients and close contacts in this community to prevent infection. As mental illness led to difficulties with mediation adherence, FDQ decoction will be provided as a daily drink with food during dining time. After treatment for one month, all the patients were detected negative and returned to their routine schedule. In this report, we summarized the procedures we took and assessed the effectiveness of FDQ in treating COVID-19.
Basic Information
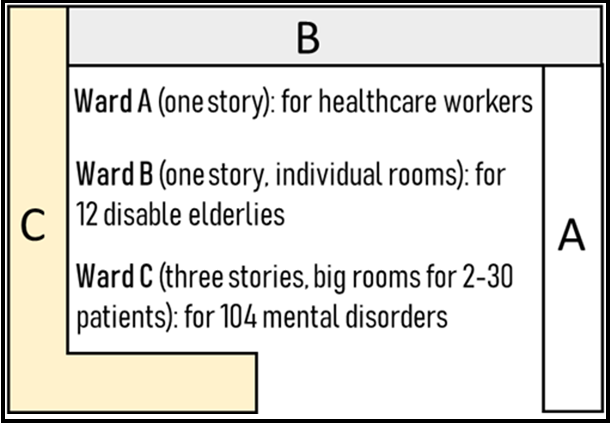
The layout of the hospital and the patients: The patients consisted of two populations. One was 12 disabled elderlies living in ward B, a one-story building. Ward B is adjacent to Ward A and Ward C and has individual patient rooms. The other one was 104 mentally disordered patients (70 males, 34 females) living in ward C, a three- story building with several big spaces in which 2 to 30 patients live in one room. Before the infection outbreak, all male patients lived on the third floor, and all female patients lived on the second floor. Most of these patients do not have cognitive ability. They don’t remember their assigned room and bed and have daily activities like watching TV and eating together in a significant activity room. It is almost impossible to quarantine these mental disorder patients at that time. The nurses and staff members who worked in Wards B and C were all living together in ward A, so ward A is also at potential risk of infection.
Figure 1: Layout of the hospital and patients
Infection Trace
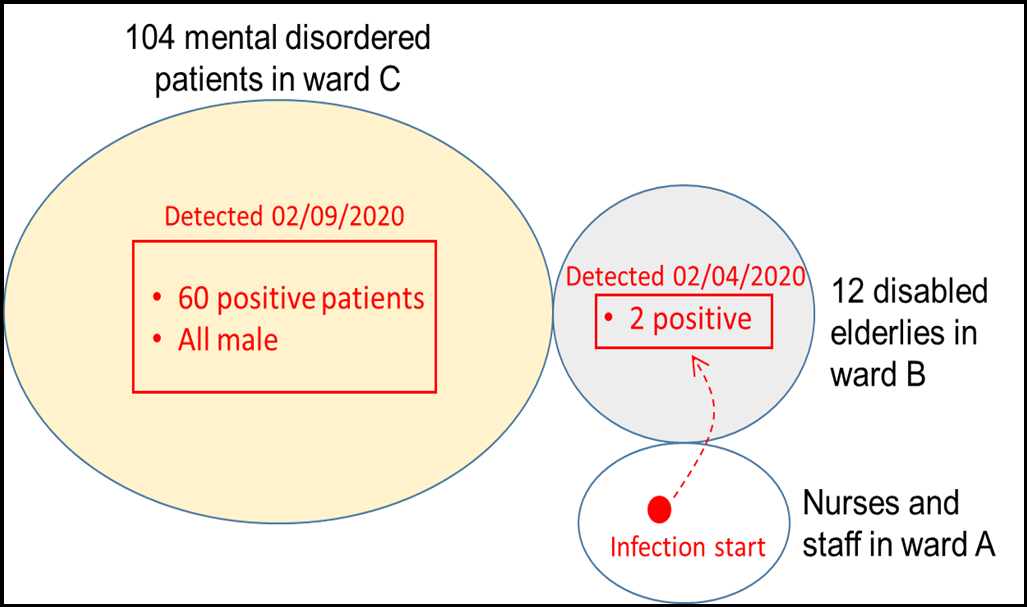
The infection originated from a nurse who worked in ward A, several days after she returned from her hometown Huanggang city, where had a severe outbreak. Two elderlies in ward B were then detected COVID-19 positive on Feb 4. These two patients were admitted to Xianning Central Hospital right away. On Feb 9, all the patients and health workers were screened for a nucleic acid test. The results confirmed a total of 60 COVID-19 positive patients. All are mental disorder male patients. The other 44 mental patients (10 males, 34 females) and the other 10 elderly patients were tested COVID-19 negative.
Figure 2: Infection trace of this large community cluster infection
Demographic information of this community: average age: (47.30 ± 13.95) yr. Number of male: 75, number of females: 41.
Clinical results at the start point: At the beginning of the outbreak, no abnormal blood routine result was reported; 2 female patients and 5 male patients had abnormal CT scan, of which six had ground-glass opacity and one had a mixture of ground-glass opacity and consolidation.
Counterplan:
- Semi-quarantined 34 female, 10 male mental disorder COVID-19 negative patients, and 60 male mental disorder COVID-19 positive patients on the first floor, the second floor, and the third floor of ward C, respectively. To avoid nosocomial infection, we set up some isolation units, which will be used to quarantine future confirmed patients.
- Built a hard partition wall between Ward A and Area B. Semi-quarantined the 10 COVID-19-negative elderlies in Ward B.
- FDQ decoction was used thrice daily for all COVID-19-positive and negative patients for treatment and prevention, 150ml each time.
- Strengthen the disinfection procedure: clean and sanitize the whole area, the ward, and patient rooms at least twice daily using Common 84 disinfectant and FDQ spray (make FDQ into low-concentration liquid and put it in a big sprayer).
- Made contingency plans for emergencies when the patient develops a severe or critical condition, accidentally falls, and when a healthcare worker is infected.
- Supply more PPE and hand sanitizer.
- Closely monitor any possible infection symptoms and measure vital signs at least once per day.
Treatment Procedure and Results:
February 10 – February 24: “Boiling period.”
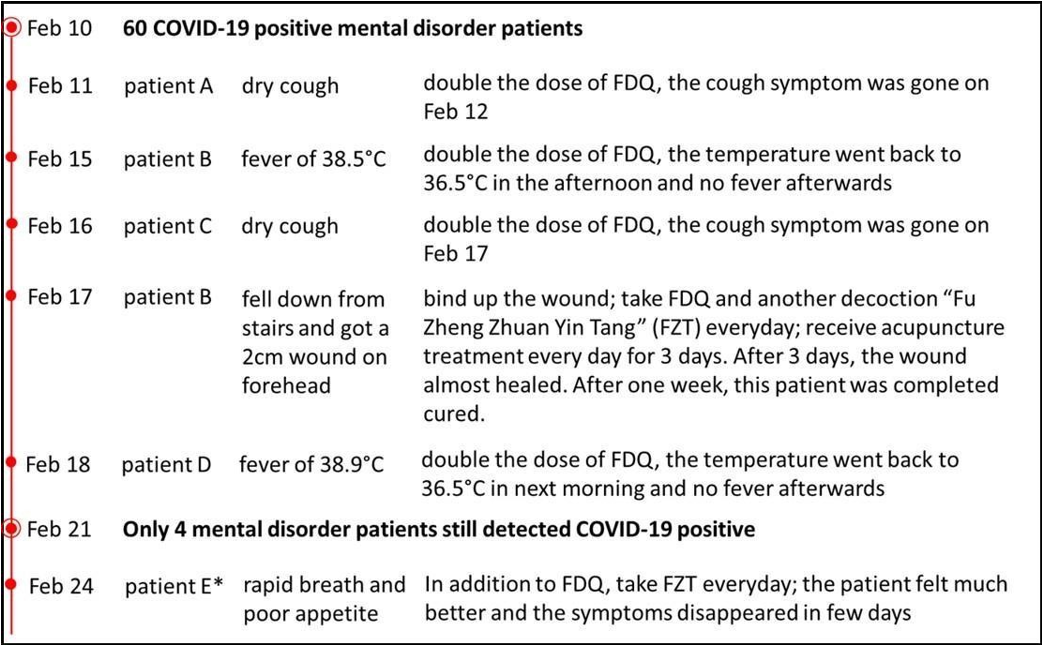
This is the period when the infection was still developing. Patients started showing typical COVID-19 symptoms, such as coughing and fever (Figure 3). In this period, several patients had dry cough or fever symptoms. After double the dose of FDQ, those symptoms disappeared in 24 hours. In more severe cases, such as when patient B was injured and patient E was critically ill, another Chinese herb decoction, “Fu Zheng Zhuan Yin Tang” (FZT), was added to the current prevention/treatment plan. After treating with FDQ and FZT, both patients recovered in a few days. On Feb 21, the second-round screening results showed that only 4 patients remained COVID-19 positive.
Figure 3: Control of emerged symptoms in boiling period
*Patient E is COVID-19 negative elderly, who is bedridden and has multiple organ failure (MOF). This patient was nearing the end of life during the boiling period. After the treatment by FDQ and FZT, she recovered and is still alive now.
February 25 – March 10: “Calming down period”
The situation was under control by Day 15. No additional cases of fever or other symptoms were found after Feb 25. However, the 4 COVID-19 COVID-19-positive patients were still at risk of having symptoms anytime. These 4 patients kept drinking FDQ and FZT every day, 3 times per day. The rest of the patients kept drinking FDQ as well for prevention.
On March 5, a third round of nucleic acid tests was conducted for all patients in wards B and C. Only 1 patient (patient F) was still COVID- 19 positive, and he had laryngeal cysts.
March 11 – March 16: “Cure period”
On March 11, for the first time, all the patients got negative test results. According to the World Health Organization’s guidelines, only after two negative test results in a row, at least 24 hours apart, a coronavirus patient is declared recovered. However, on March 12, when we did the nucleic acid test again, two patients tested positive again. One is patient F, who had laryngeal cysts. The other one is patient G, who had cholecystitis. After being examined by Chinese medicine pulse diagnosis, these two patients were prescribed personalized Chinese herbal decoction for treatment. On March 14, 15 and 16, these patients were tested again by nucleic acid screening. All patients were negative in three tests and, after that, were considered cured. This large community cluster outbreak of COVID-19 was completely controlled.
Discussion
Psychiatric inpatients are particularly vulnerable to the transmission and effects of COVID-19. There is no case reported yet on treating a cluster infection in psychiatric hospitals. In the present large community cluster infection case, all 60 COVID-19-positive patients are mental disorder patients, of which some also have chronic underlying diseases. Because of the community characterization, enforced quarantine and standard treatment in the hospital is not feasible. Therefore, this compromised prevention and treatment plan by using FDQ was implemented.
The whole treatment period lasted over 1 month. In the beginning, it was the boiling period when symptoms and complications appeared. The most common symptoms observed are fever and cough. Those symptoms usually disappear in 24 hours after double the dose of FDQ. There were 4 out of 60 COVID-19 patients who showed symptoms, so the asymptomatic proportion was > 90 %. This ratio is much higher than the reported proportion of 18 %-80 % [10,11]. Moreover, although this population is at higher risk for developing more serious complications, none had developed severe COVID-19 illness, and no other direct contacts were infected afterward. In less than 2 weeks, on February 21, only 4 patients remained COVID-19 positive. We gave the credit to several reasons: 1. we intervened in this cluster infection at the early stage of the outbreak. 2. FDQ is very effective in treating NCP (novel coronavirus pneumonia), especially for mild and moderate symptoms. 3. FDQ can prevent the infection of COVID-19 in close contact so that this cluster infection doesn’t spread further. One COVID-19-negative elderly patient, who had symptoms of rapid breath, poor appetite, and other historical complications, was also treated with FDQ and FZT. We successfully saved her life after the treatment. This is consistent with the clinical results we collected while applying FDQ, in which FDQ is potent in treating other COVID-19 non-relevant symptoms in the respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract (refer to Dr. Wang’s other COVID-19 paper).
After treatment for 2 weeks, this cluster infection was entirely under control. No additional cases of fever or other symptoms were found after Feb 25. For the remaining 4 intractable positive patients, another Chinese herb decoction, FZT, was added to the treatment plan. On March 5, there was only 1 patient detected laboratory positive. This patient was later seen as harmful on March 11 but back to positive again on March 12 with another patient. The alternating results between positive and negative have been reported in many cases worldwide [12,13]. It may be due to the sensitivity limit of the test. Some patients could stick in this swing situation for over 50 days. Fortunately, after taking personalized Chinese herbal decoction, these two patients were detected negative thrice on March 14, 15, and 16. This is the first time using TCM only to treat COVID-19 cluster infection, and the clinical benefit was better than any known western medicine.
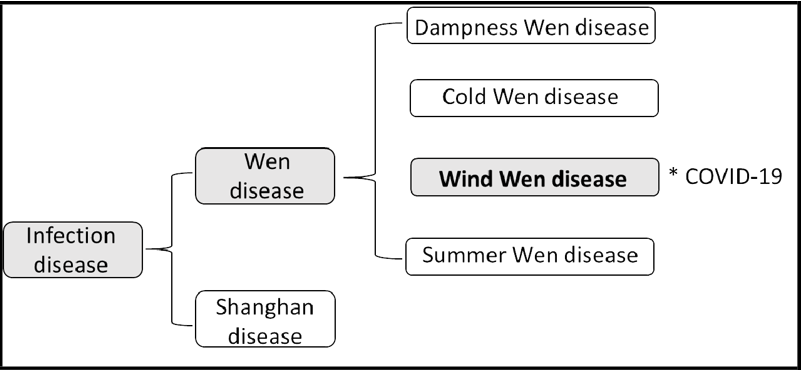
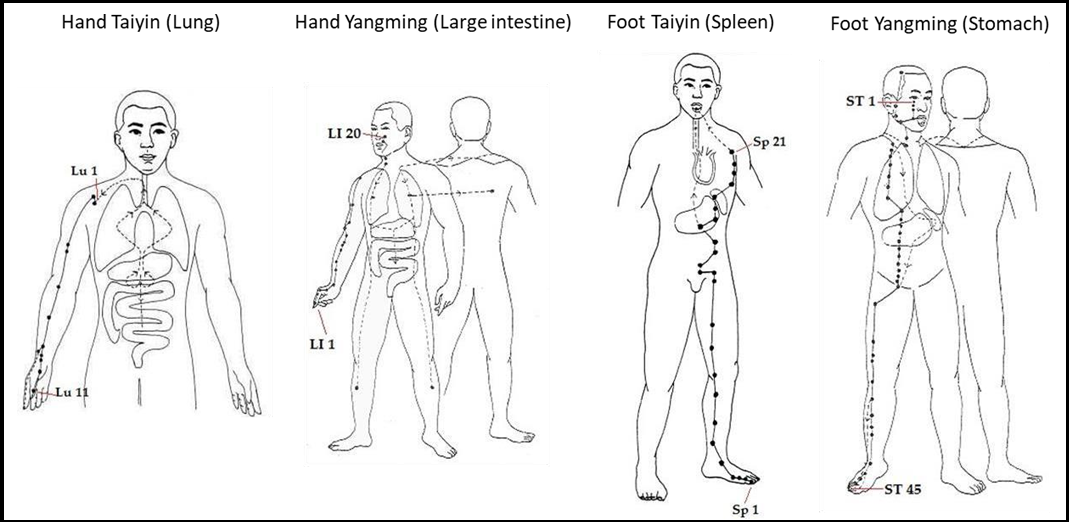
What is COVID-19 from the viewpoint of TCM? There are two types of infectious diseases in TCM: “Shanghan disease,” which occurs instantly after the infection without an incubation period, and “When disease,” which occurs after an incubation period, usually more than 7 days. The Wen disease can be further divided into “Cold Wen disease,” “Dampness Wen disease,” “Wind Wen disease,” “Summer Wen disease,” and “Dryness Wen disease.” Based on the COVID-19 characteristics of quick spreading and its multi-organ impact, and the pulse diagnosis on hundreds of COVID-19 patients, we defined it as a kind of “Wind Wen disease” (Figure 4). The impacted meridians and their corresponding organs are Hand Taiyin, corresponding to the lung; Han Yangming, corresponding to the large intestine; Foot Taiyin, corresponding to Spleen; and Foot Yangming, related to the stomach. (Figure 5)
Figure 4: Definition and classification of COVID-19 in TCM
Figure 5: Impacted meridians and their corresponding organs by COVID-19 in TCM
FDQ was invented right at the beginning of the outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan on January 20th. After successfully curing a 70-year-old woman with a long history of diabetes and a family cluster infection, it was included in the official guideline for COVID-19 treatment in several counties in Xianning City. It is very effective in treating NCP (novel coronavirus pneumonia) patients at home and in hospitals.
This is the first time using FDQ to treat extensive community cluster infection in a particular community. We raised the concept of a “whole community preparedness and treatment” (WCPT) approach against COVID-19 from this successful case. WCPT is a multifaceted strategy that includes the following:
1. Separation: Confirmed patients, suspected patients, and direct contacts should be quarantined right away when infection is confirmed. If quarantine is not feasible, they must be separated as much as possible in different activity zones, away from other people.
2. All: Everyone in the community, including patients, direct contacts, and high-risk and vulnerable populations, takes FDQ daily for treatment and prevention. In our clinical observation, FDQ is very effective in the prevention and treatment of mild and moderate COVID-19 patients. Other medical intervention is only needed for severe and critical conditions.
3. Early: The treatment must start as early as possible when infection is confirmed, even if no symptoms appear. There was no patient treated by FDQ at an early stage of the disease that developed into a severe case.
4. Reinforcement: After the patient is cured, FDQ can still be taken for another 14 days to prevent the risk of re-detectable positive.
By following WCPT strategy and using FDQ as the main treatment approach, we achieved 98.21% cure rate in Xianning city. Xianning was also the first prefecture-level city that cured all patients in Hubei Province. (Reference to our other paper about FDQ application in hospitals). It has been wildly used for prevention of COVID-19 infection in high-risk populations such as frontline healthcare workers, police department, senior houses in many cities in China (8). While the global health is still facing a serious challenge with COVID-19 epidemic, our success in controlling in large community is of great guiding significant.
Since the end of 2022, China has liberalized the containment of the epidemic, and FDQ has been further applied on a large scale, with very encouraging results. From our clinical observation, FDQ can even play a good role in other infectious diseases of the lung, even non-infectious diseases, and we will further summarize relevant experience.
Conclusion
FDQ is an effective formula for the treatment of acute pulmonary infectious diseases and is worthy of further clinical promotion.
Funding sources
This paper was funded by 1) the key project of Xianning Municipal Science and Technology Project "Research and Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine Modernization of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Prescription FDQ" (2020SFYF01); 2) Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province "Study on Pharmacological Action and Tablet Preparation Technology of FDQ " (2020CFB868).
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Ethical Statement
The authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
All procedures involving human subject were approved by the institutional review board at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hubei College of Science and Technology.
References
- WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic.
- Druss BG (2020) Addressing the COVID-19 Pandemic in Populations With Serious Mental Illness. Druss BG. JAMA Psychiatry. 77(9): 891-892.
- Xiang YT, Zhao YJ, Liu ZH, Li XH, Zhao N, et al. (2020) The COVID-19 outbreak and psychiatric hospitals in China: managing challenges through mental health service reform. Int J Biol Sci. 16(10): 1741–1744.
- Zhu Y, Chen L, Ji H, Xi M, Fang Y, et al. (2020) The Risk and Prevention of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Infections Among Inpatients in Psychiatric Hospitals. Neurosci. Bull. 36(3): 299– 302.
- Campbell D, Grierson J (2020) Psychiatrists fear surge of Covid- 19 cases in UK mental health units. The Guardian.
- NBC News. Coronavirus in a psychiatric hospital: 'It's the worst of all worlds.
- Brown C, Ruck Keene A, Hooper CR, O'Brien A (2020) Isolation of patients in psychiatric hospitals in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic: An ethical, legal, and practical challenge. Int J Law Psychiatry. 71: 101572.
- Chinese Daily (2020) TCM proving potent force in contagion fight.
- Xinhua News. TCM has proved effective in fighting COVID-19 in Xianning city
- Mizumoto K, Kagaya K, Zarebski A, Chowell G (2020) Estimating the asymptomatic proportion of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases on board the Diamond Princess cruise ship, Yokohama, Japan, 2020. Euro Surveill. 25(10): 2000180.
- Day M (2020) Covid-19: Four Fifths of Cases Are Asymptomatic, China Figures Indicate. BMJ. 369: m1375.
- Lemos G (2020) A Florida man has been stuck on a ship for 62 days in an Italian port. He’s been tested 8 times for coronavirus.
- Scribner H (2020) This Canadian woman says she’s tested positive for coronavirus 8 different times.